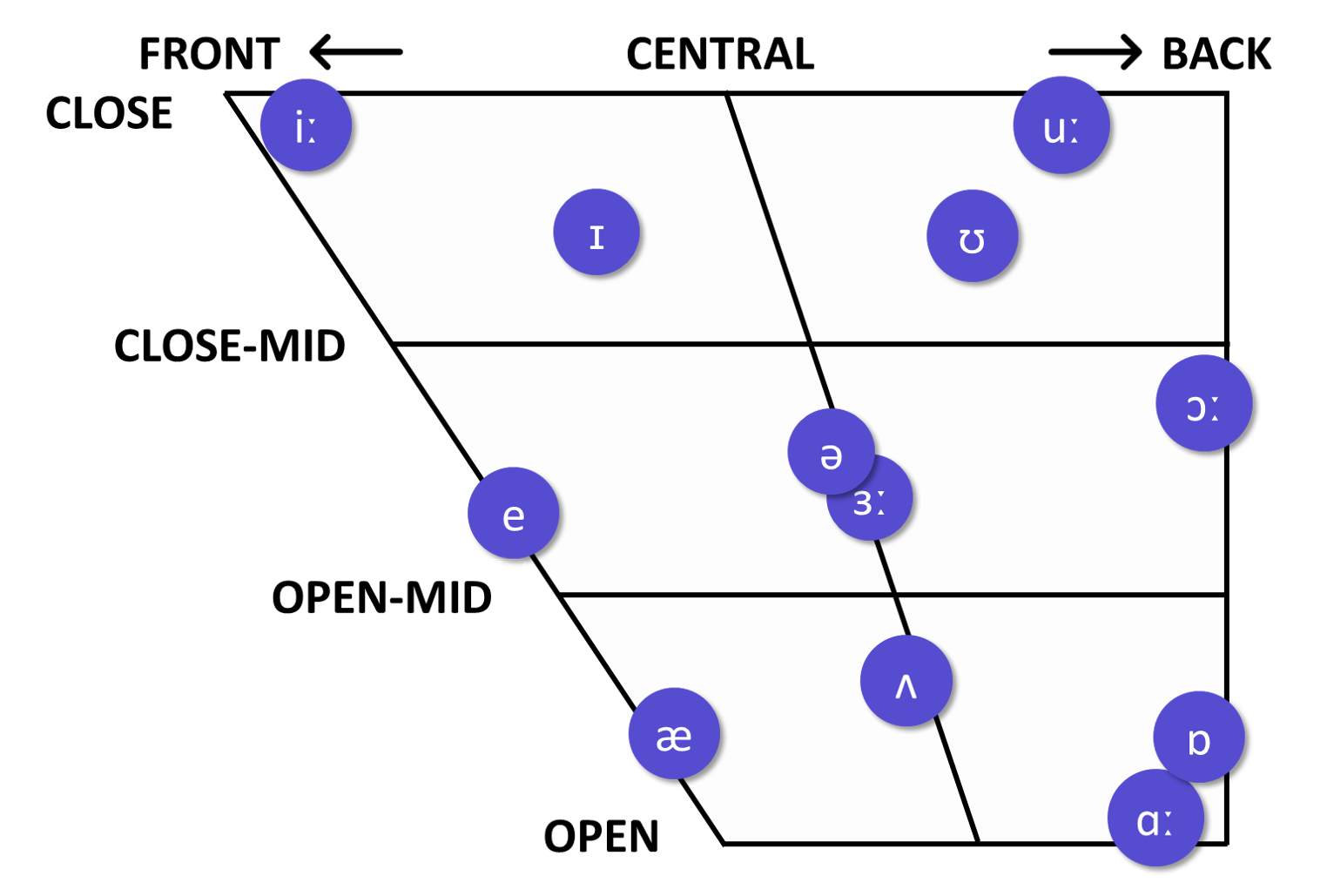
Interactive English Vowel Chart
♦ English Monophthongs
HVPT_English vowels
high front long vowel /iː/
beat
bead
heat (Female)
heed
peed
feed
feed (Female)
veed*
weed
keyed
geed*
*Veed and geed are not real words.
near-high front short vowel /ɪ/
bit
bit (Female)
bid
hit
hit (female)
hid
hid (Female)
pid*
fid
vid*
wid*
kid
kid (Female)
gid
*Pid, vid and wid are not real words.
high back long vowel /uː/
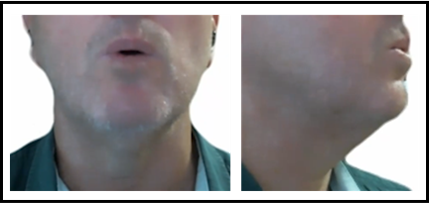
boot
boot (Female)
cooed
near-high back short vowel /ʊ/
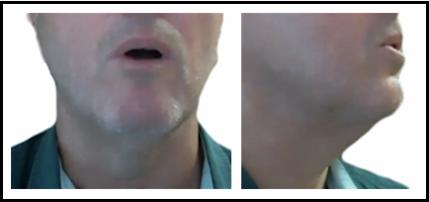
hood
hood (Female)
could
could (Female)
mid-central short vowel /ə/
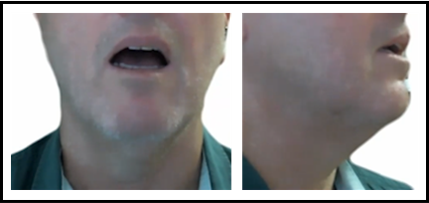
about
about (Female)
official
official (Female)
letter
letter (Female)
comma
comma (Female)
low-mid central long vowel /ɜː/
bird
hurt
hurt (Female)
herd
herd (Female)
mid front short vowel /e/
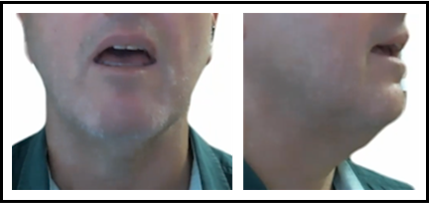
bet
bed
het
head
head (Female)
ped*
fed
fed (Female)
ved*
wed
ked
ged*
*Ped, ved and ged are not real words.
near-low front short vowel /æ/
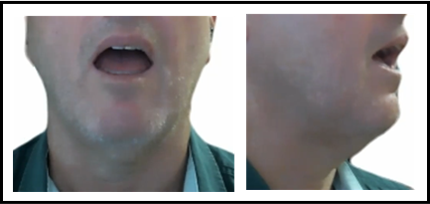
bat
bad
hat
hat (Female)
had
had (Female)
pad
fad
fad (Female)
vad*
wadd**
cad
cad (Female)
gad
gad (Female)
*Vad is not a real word.
**A pseudo word 'wadd' is used here, instead of the real word 'wad' which is pronounced as /wɒd/.
high-mid back long vowel /ɔː/
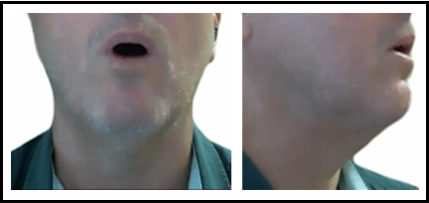
bought
bored
cord
cord (Female)
low back short vowel /ɒ/
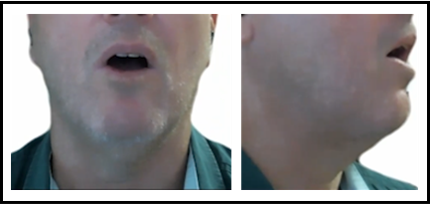
bod
cod
cod (Female)
low back long vowel /ɑː/
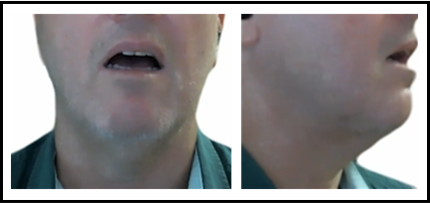
barred
near-low central short vowel /ʌ/
but
but (Female)
bud
HVPT_Cantonese vowels
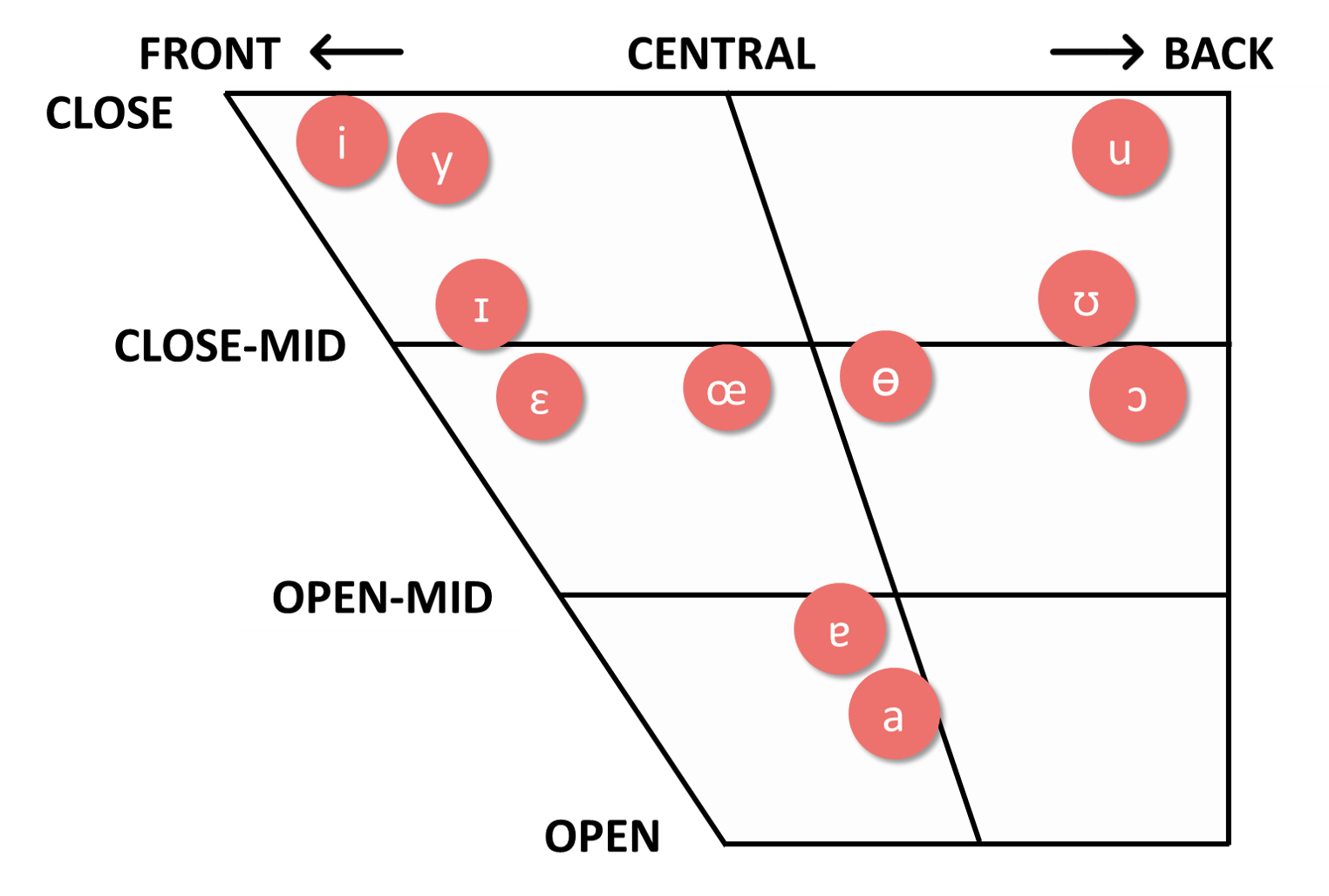
Close front vowel [i]
Close front vowel [y]
Close back vowel [u]
Mid front vowel [ɛ]
Mid front vowel [œ]
Mid back vowel [ɔ]
Open central vowel [a]
Close-mid front vowel [ɪ]
Mid central vowel [ɵ]
Close-mid back vowel [ʊ]
Open central vowel [ɐ]
Notes:
1. The vowel chart is adapted from the one used by Zee (1999).
2. Click HERE to view the original chart.
HVPT_Mandarin vowels
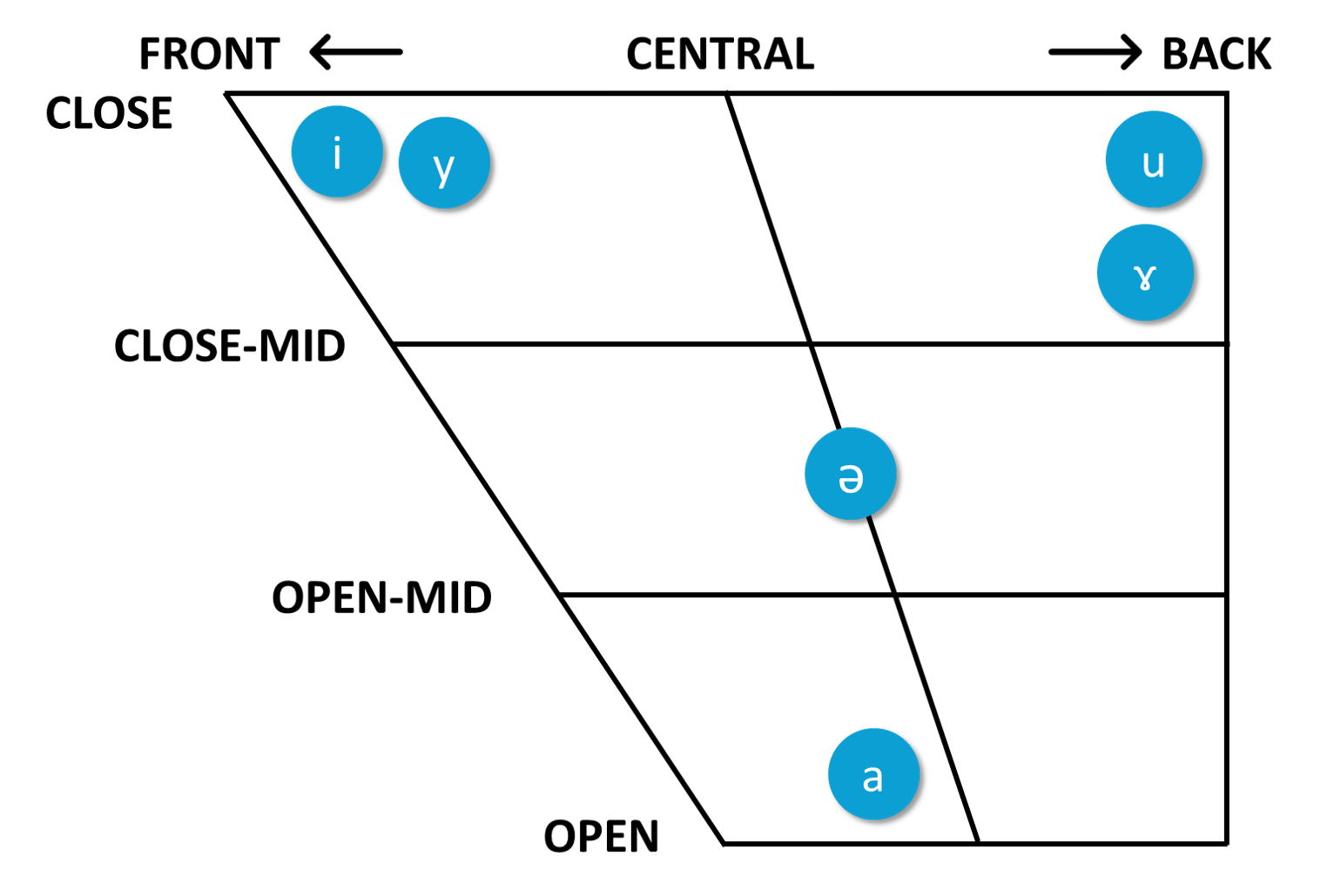
a
a
(Pinyin: [ɑ] as in '爬'[pɑ2])
[ha2]
Female:
Male:
ɤ
ɤ
(Pinyin: [e] as in '河' [he2])
Female:
Male:
i
i
(Pinyin: [i] as in '鼻'[bi2])
Female:
Male:
y
y
(Pinyin: [ü] as in '驴' [lǘ])
[hü2]
Female:
Male:
u
u
(Pinyin: [u] as in '湖' [hú])
Female:
Male:
ə
ə
(Pinyin: [e] as in '儿' [ér])
(*[ə] is rhotacized as [ɚ].)
[her2]
Female:
Male:
Notes:
1. The vowel chart is adapted from the one used by Lee and Zee (2003).
2. Click HERE to view the original chart
♦ English Diphthongs
HVPT_English diphthongs
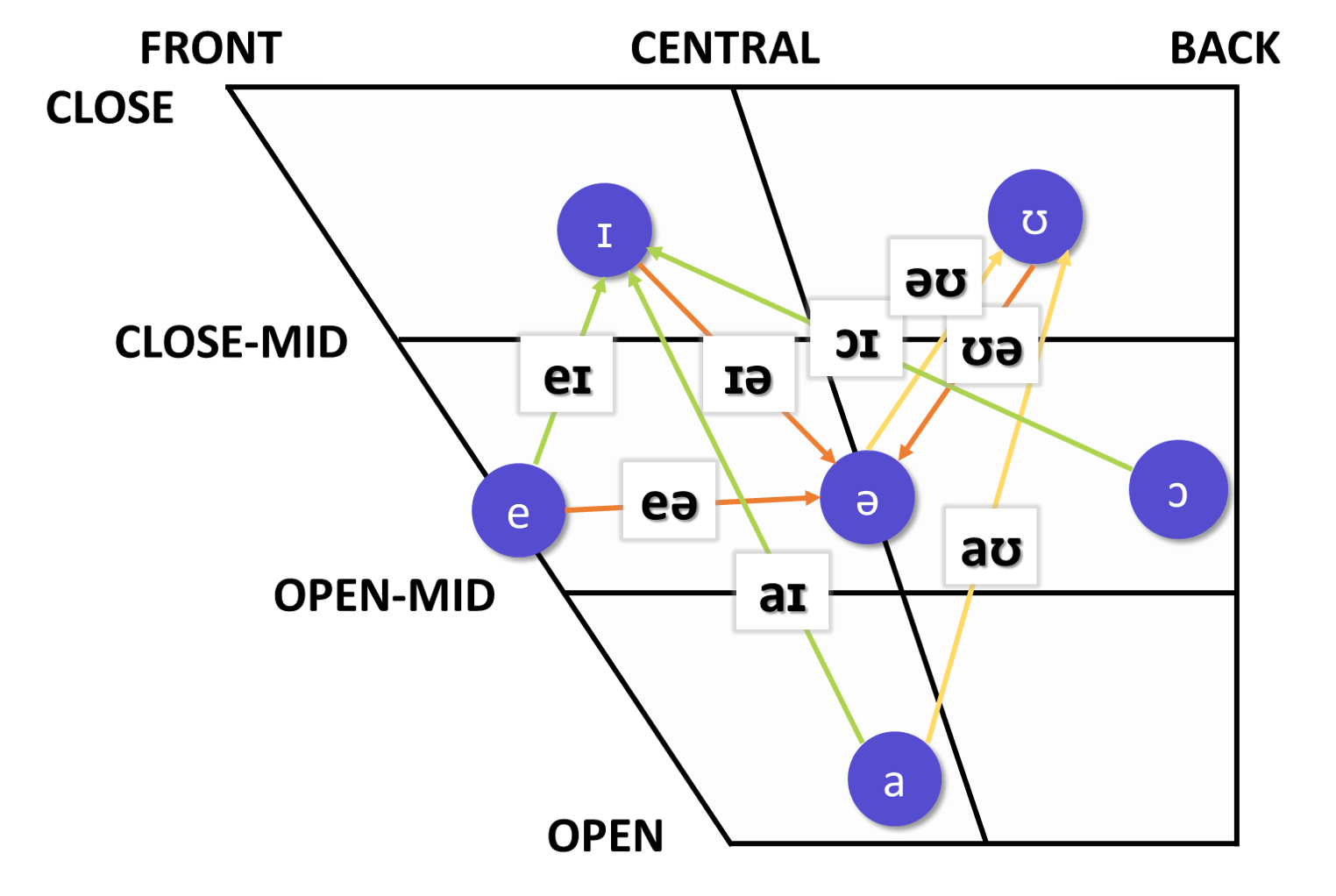
closing diphthong /eɪ/
bait
bade*
hate
hate (Female)
hade
paid
fade
fade (Female)
vade
vade (Female)
wade
cade
gade**
*Bade is the past tense of 'bid', which can be pronounced in two ways (i.e., /bæd/ and /beɪd/).
**Gade is not a real word.
closing diphthong /aɪ/
bite
bide
high
high (Female)
height
height (Female)
hide
hide (Female)
closing diphthong /ɔɪ/
boy
closing diphthong /əʊ/
boat
bode
coat
coat (Female)
code
code (Female)
closing diphthong /aʊ/
bout
centering diphthong /ɪə/
beard
centering diphthong /eə/
bare/bear
bared
centering diphthong /ʊə/
tour
◊ Notes:
1. The vowel charts are adapted from those used by Roach (2004).
2. Recordings were made by 3 male native speakers of British English or from 5 popular online dictionaries (including Cambridge Dictionary, Oxford Dictionary, Longman Dictionary, Collins Dictionary, and Macmillan Dictionary). All the vowel sounds are pronounced in a Southern British English accent.
Phonetic Training_English vowels_three voices
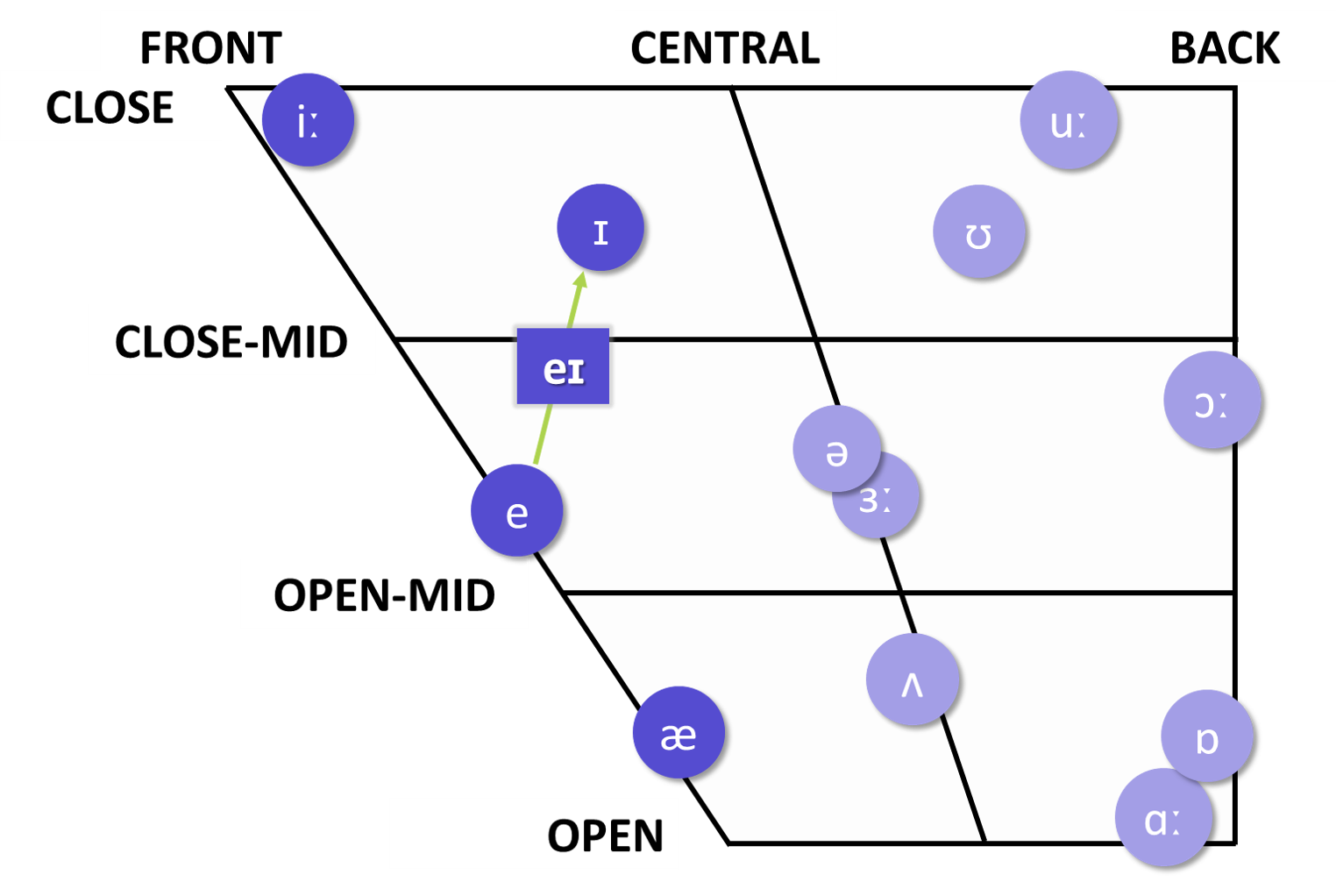
high front long vowel /iː/

heat
heed
hee*
*'Hee' is not a real word here. Its pronunciation is /hiː/ as in word 'heat'/hiːt/.
near-high front short vowel /ɪ/

hit
hid
hi*
*'Hi' is not a real word here. Its pronunciation is /hɪ/ as in word 'hit'/hɪt/.
mid front short vowel /e/

het
head
he*
*'He' is not a real word here. Its pronunciation is /he/ as in word 'hen'/hen/.
near-low front short vowel /æ/

hat
had
ha*
*'Ha' is not a real word here. Its pronunciation is /hæ/ as in word 'hat'/hæt/.
closing diphthong /eɪ/
hate
hade
hay
*Bade is the past tense of 'bid', which can be pronounced in two ways (i.e., /bæd/ and /beɪd/).
Click HERE to view the original chart
Self-access Perception Tasks
*for English front vowels only
Vowel Sounds in Continuous Speech
♦ Reading of a passage
Notes: Letters/letter combinations in different colors indicate different vowel sounds they are pronounced (i.e., blue - /iː/, green - /ɪ/, orange - /e/, pink - /æ/ and purple -/eɪ/).
The Boy Who Cried Wolf
There was once a poor shepherd boy who used to watch his flocks in the fields next to a dark forest near the foot of a mountain. One hot afternoon, he thought up a good plan to get some company for himself and also have a little fun.
UK1
UK2
UK3
(Please focus on the sound underlined)
• shepherd /ˈʃep.əd/
UK1
UK2
UK3
• field /fiːld/
UK1
UK2
UK3 (fields)
• forest /ˈfɒr.ɪst/
UK1
UK2
UK3
• plan /plæn/
UK1
UK2
UK3
*Tips on how to practise: Try to embed the target sound into different phonetic environments, for example, you may try to pronounce the /æ/ sound linked with different consonant clusters either as the initial or final sound of a word, such as 'fl-' (flash), '-sp' (grasp). In this passage, /æ/ sound is linked with the initial consonant cluster 'pl' (as in 'plan').
• flash /flæʃ/
UK1
Raising his fist in the air, he ran down to the village shouting ‘Wolf, wolf.’ As soon as they heard him, the villagers all rushed from their homes, full of concern for his safety, and two of his cousins even stayed with him for a short while.
UK1
UK2
UK3
This gave the boy so much pleasure that a few days later he tried exactly the same trick again*, and once more he was successful. However, not long after, a wolf that had just escaped from the zoo was looking for a change from its usual diet of chicken and duck.
*The word 'again' has two pronunciations (i.e., /əˈɡen/ & /əˈɡeɪn/)
UK1
UK2
UK3
• gave /ɡeɪv/
UK1
UK2
UK3
• pleasure /ˈpleʒ.ər/
UK1
UK2
UK3
• same /seɪm/
UK1
UK2
UK3
• later /ˈleɪ.tər/
UK1
UK2
*Tips on how to practise: It's a good way to pracise the sound contrasts in minimal pairs, for example, later-letter; later-litter; letter-litter; litter-liter.
• later-latter-letter-litter-liter
UK1
So, overcoming its fear of being shot, it actually did come out from the forest and began to threaten the sheep. Racing down to the village, the boy of course cried out even louder than before.
UK1
UK2
UK3
• sheep /ʃiːp/
UK1
(sheep-ship)
UK2
UK3
• did /dɪd/
UK1
(extracted from word-reading task)
UK2
UK3
*Tips on how to practise: In addition to listening to the recordings produced by the 3 native English speakers on our website, you can also make use of a platform named YouGlish to get access to recordings from more native speakers. Below are the sounds extracted from YouGlish.
did
(from YouGlish)
sheep
(from YouGlish)
Unfortunately, as all the villagers were convinced that he was trying to fool them a third time, they told him, ‘Go away and don’t bother us again*.’ And so the wolf had a feast.
*The word 'again' has two pronunciations (i.e., /əˈɡen/ & /əˈɡeɪn/)
U1
UK2
UK3
• feast /fiːst/
UK1
UK2
UK3
(from YouGlish)
*Tips on how to practise: Still, you may pracise the sound contrasts such as /iː-ɪ/ in various minimal pairs, like 'feast-fist', 'least-list', 'eat-it', 'he's-his', etc, and then try to pronounce these words in different contexts gradually from individual word, phrase, sentence and then to dialogue and free speech.
• least-list
UK1
• eat-it
UK1
• he's-his
UK1