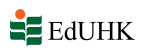4.3.1. What is intonation?
| Roach (2000, p.150) | → No definition is completely satisfactory
→ The pitch of the voice plays the most important part |
| Kenworthy (1987, p.11) | → intonation = the melody of speech |
| Teschner & Whitley (2004, p.64) | → Intonation is a series of pitches sung over a whole utterance |
| Celce-Murcia, Brinton & Goodwin (1996, p.184) | → If pitch = individual tones of speech
then intonation = the entire melodic line → Intonation involves the rising and falling of the voice to various pitch levels during the articulation of an utterance. |
4.3.2. Cantonese vs English intonation
| Chinese
(including Cantonese, Putonghua & other regional languages in China) |
English |
| tone language | intonation language |
| The tone of each character contributes to lexical meanings | The tones vary over a stretch of utterance, and contribute to accentual features, or convey attitudinal meanings. |
Intonation is determined by many elements like pitch, energy, duration, tempo and sound quality. Pitch plays a more important role than the remaining elements. As English is an intonational language, the intonation expresses speakers' emotion and attitude. Native speakers use different intonations in different sentence types.
In Praat, we mainly use pitch contour to indicate different tones, like falling and rising tones.
- Select the sound in object list
- Click "View & Edit"
- "Pitch" → tick "show pitch"
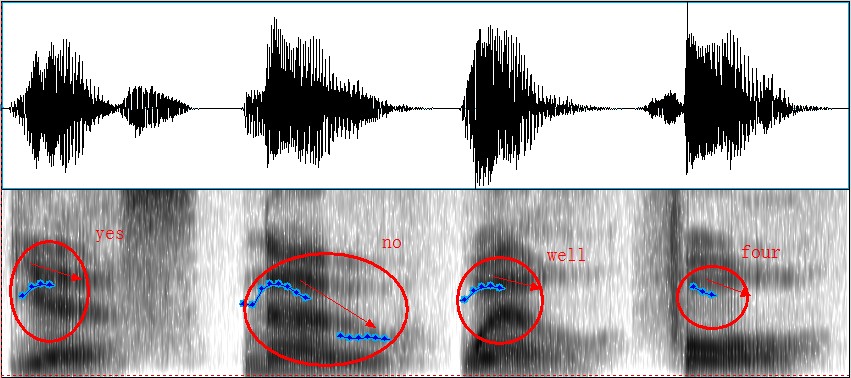
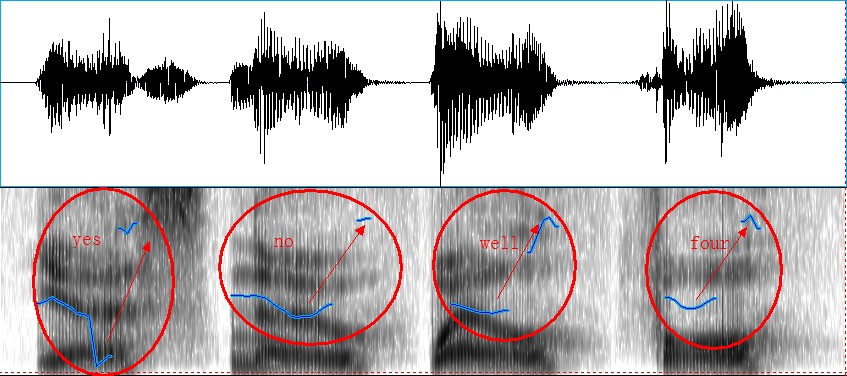
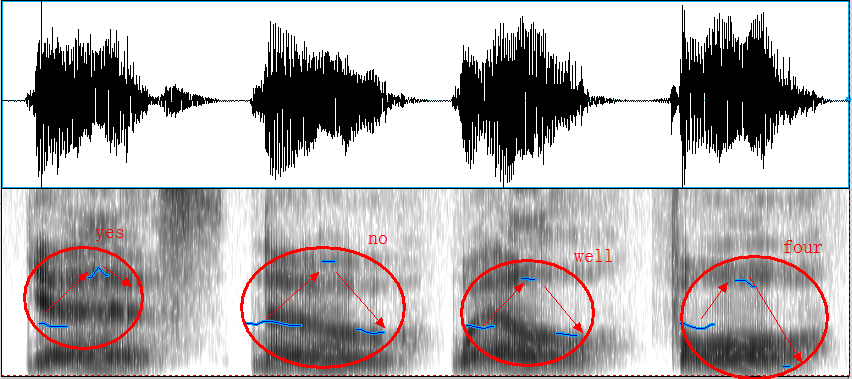
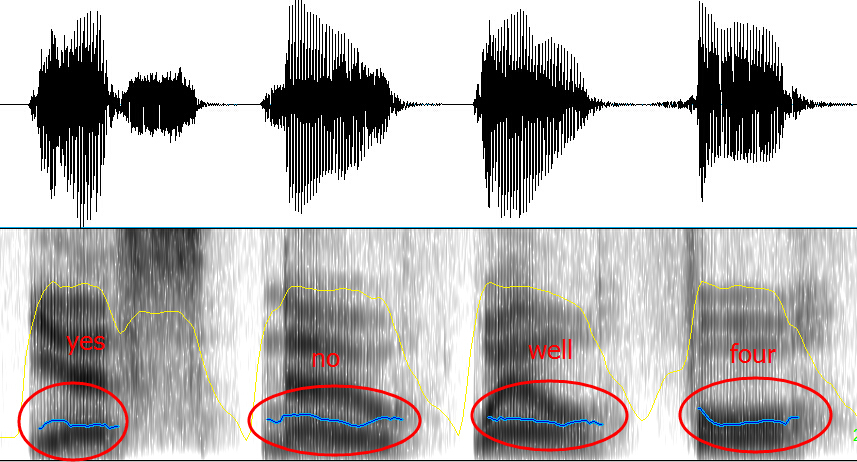
4.3.3. Common types of intonation in English
4.3.4. Communicative functions of English intonation
A. The accentual function
to indicate the focus of the information
B. The attitudinal function
to indicate the speaker’s attitude
| The falling tone suggests: | • finality, completion
• certainty, belief in the content of the utterance • speaker-dominance |
| The rising tone suggests: | • more to follow
• querying, uncertainty • encouraging • speaker-deference – the speaker does not know → asks – does not have authority → requests |
| The level tone suggests: | • routine
• boredom, no interest |
C. The grammatical function
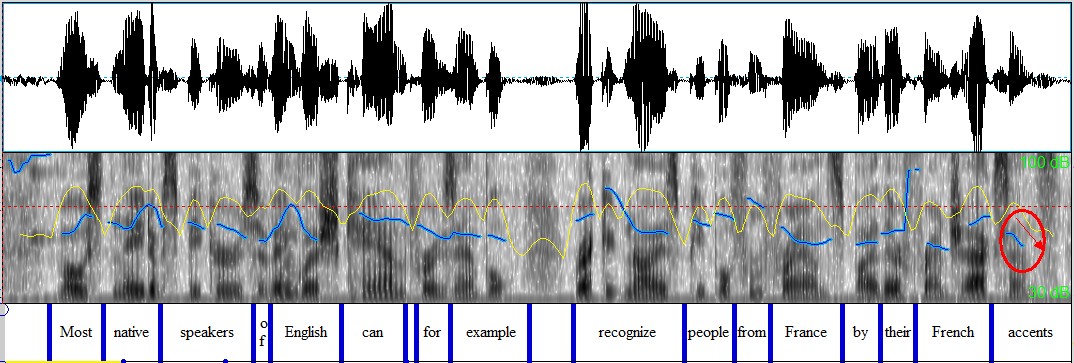
a) Statements: falling tone
Most native speakers of English can, for example, recognize people from France by their French accents. ↘
Figure 4. 19
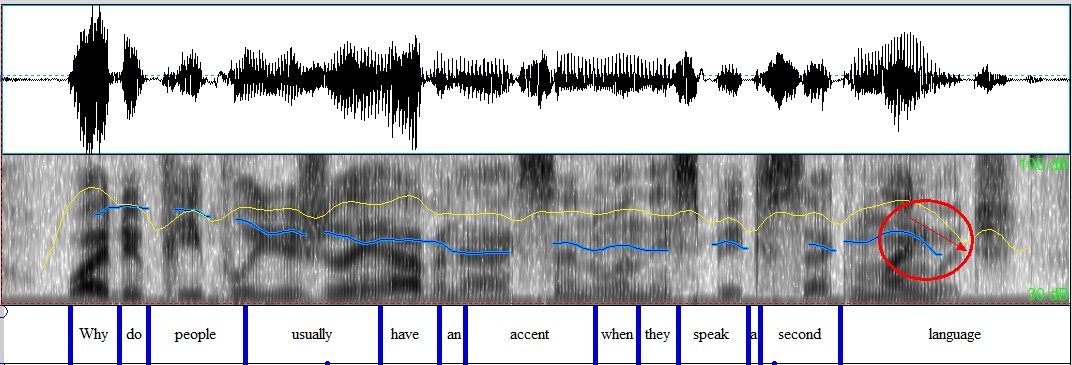
b)Wh- Questions: normally falling tone
Why do people usually have an accent when they speak a second language? ↘
Figure 4.20
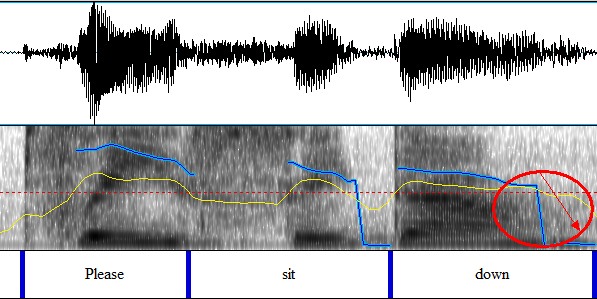
c) imperative sentence:falling tone
Please sit down. ↘
Figure 4.21
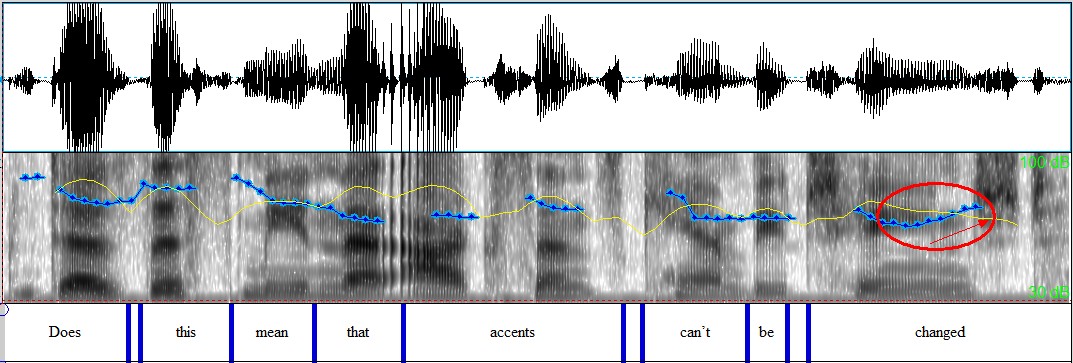
d) Yes/No Questions: normally rising tone
Does this mean that accents can’t be changed? ↗
Figure 4.22
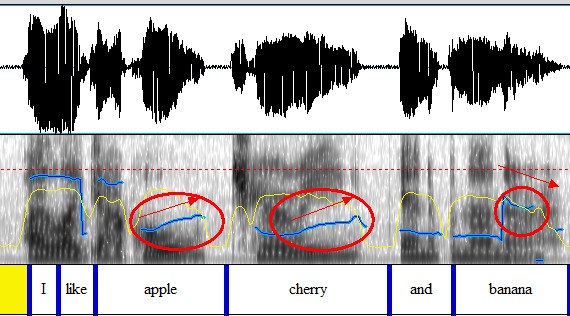
e) Listing: combination of rise & fall
I like apple, ↗ cherry,↗ and banana.
Figure 4.23
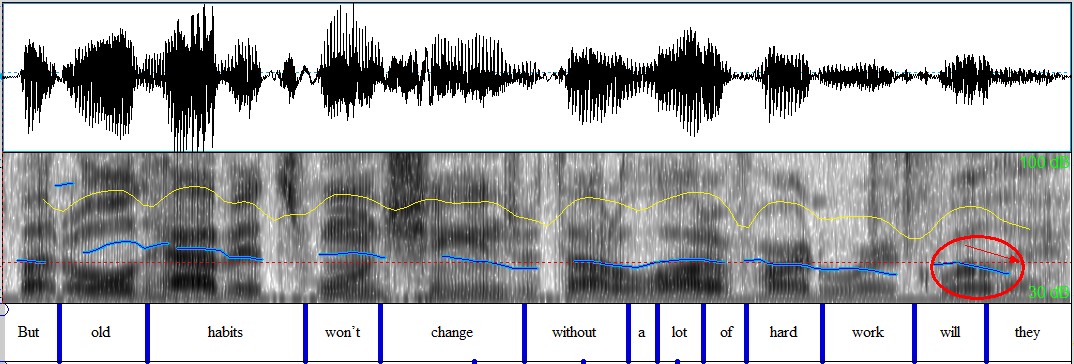
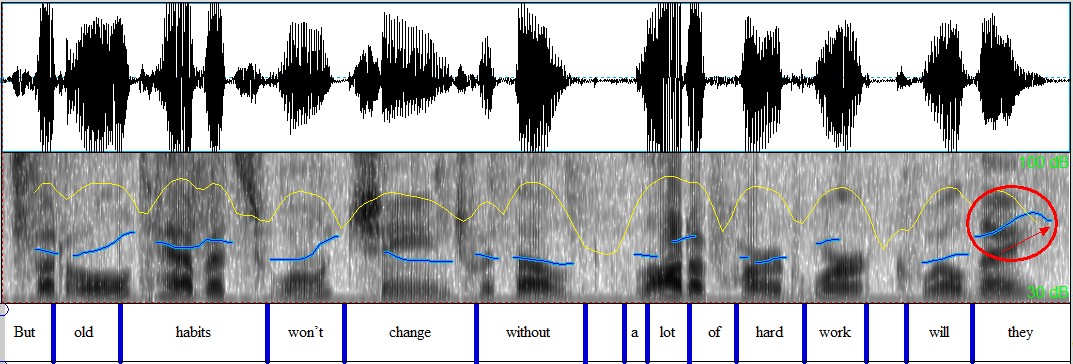
f) Tag questions: rising and falling tone
Falling tone → the speaker is quite certain, only seeking confirmation / agreement
Rising tone → the speaker is unsure, a genuine request for more information
But old habits won’t change without a lot of hard work, ↘ will they? ↘
Figure 4.24
Another possibility:
But old habits won’t change without a lot of hard work, ↘ will they? ↗
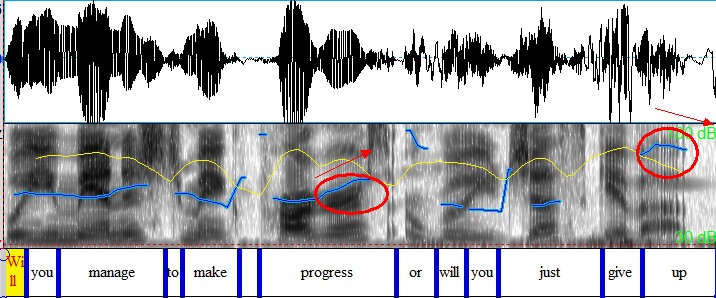
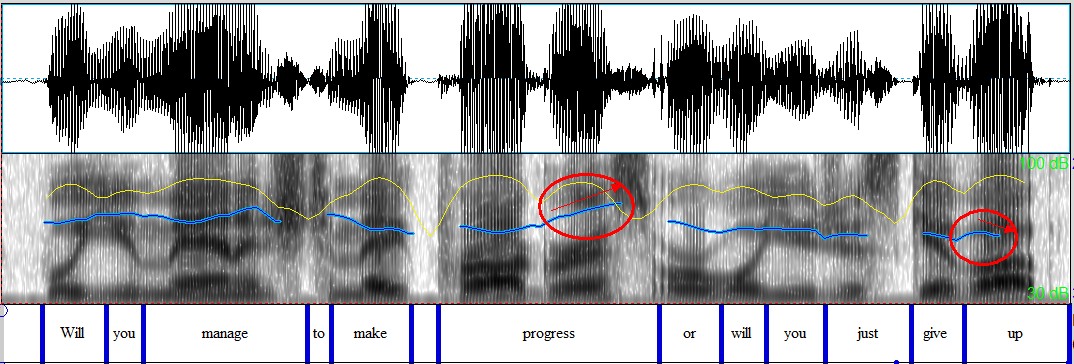
g) Closed-choice alternative questions: combination of rise & fall
Will you manage to make progress, ↗or will you just give up? ↘
Hits: 6832